디자인 패턴 톺아보기 - Prototype Pattern
Updated:
1. 프로토타입 패턴(Prototype Pattern) 이란?
GOF 에서 말하는 프로토타입 패턴의 목적은 아래와 같습니다.
Specify the kinds of objects to create using a prototypical instance, and create new objects by copying this prototype.
원형이 되는(prototypical) 인스턴스를 사용하여 생성할 객체의 종류를 명시하고, 이렇게 만든 견본을 복사해서 새로운 객체를 생성합니다.
1.1. 구조
Sample / Sequence Diagram
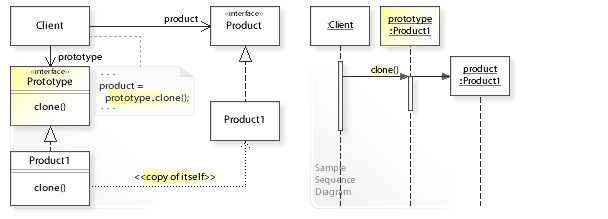
- Prototype
- 자신을 복제하는 데 필요한 인터페이스를 정의합니다.
- ConcretePrototype
- 자신을 복제하는 연산을 구현합니다.
- Client
- 원형에 자기 자신의 복제를 요청하여 새로운 객체를 생성합니다.
1.2. 사용 방법
- 사용자는 원형 클래스에 스스로 복제하도록 요청합니다.
1.3. 장/단점
- Advantages (+)
- Allows adding and removing prototypes dynamically at run-time.
- Allows instantiating dynamically loaded classes.
- Provides a flexible alternative to Factory Method.
- Disadvantages (–)
- Can make the implementation of the clone operation difficult.
1.4. 고려사항
- Consider the left design (problem):
- Which object to create is specified at compile-time.
- Consider the right design (solution):
- Which object to create is specified at run-time.
2. 프로토타입 패턴(Prototype Pattern) 사용예시
프로토타입 패턴은 제품의 생성, 복합, 표현 방법에 독립적인 제품을 만들고자 할 때 사용합니다.
- 인스턴스화할 클래스를 런타임에 지정할 때
- 제품 클래스 계통과 병력적으로 만드는 팩토리 클래스를 피하고 싶을 때
- 클래스의 인스턴스들이 서로 다른 상태 조합 중에 어느 하나일 때 원형 패턴을 씁니다. 이들을 미리 원형으로 초기화해 두고, 나중에 이를 복제해서 사용하는 것이 매번 필요한 상태 조합의 값들을 수동적으로 초기화하는 것보다 더 편리할 수도 있습니다.
2.1. GOF 패턴
2.1. Prototype
interface Prototype {
Product clone();
}
2.1.2. ConcretePrototype
interface Product {
String getName();
}
class Computer implements Product, Prototype {
private String name;
public Computer(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Computer(Computer c) {
this.name = c.getName();
}
@Override
public Product clone() {
return new Computer(this);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
class Notebook implements Product, Prototype {
private String name;
public Notebook(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Notebook(Notebook n) {
this.name = n.getName();
}
@Override
public Product clone() {
return new Notebook(this);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
2.1.3. Client
class Client {
private Product product;
private Prototype prototype;
public Client(Prototype prototype) {
this.prototype = prototype;
}
public void changePrototype(Prototype prototype) {
this.prototype = prototype;
}
public String operation() {
product = prototype.clone();
return "Client Cloning " + prototype.getClass().getSimpleName() + ".\n[" + product.getName() + "] object copied.";
}
}
2.1.4. Main
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Client client = new Client(new Computer("Computer"));
System.out.println(client.operation());
client.changePrototype(new Notebook("Notebook"));
System.out.println(client.operation());
}
}
결과는 아래과 같습니다.
Client Cloning Computer.
[Computer] object copied.
Client Cloning Notebook.
[Notebook] object copied.
2.2. GOF 패턴 2
하나의 Client
참고 자료
Leave a comment