디자인 패턴 톺아보기 - Mediator Pattern
Updated:
1. 중재자 패턴(Mediator Pattern) 이란?
GOF 에서 말하는 중재자 패턴의 목적은 아래와 같습니다.
Define an object that encapsulates how a set of objects interact. Mediator promotes loose coupling by keeping objects from referring to each other explicitly, and it lets you vary their interaction independently.
한 집합에 속해있는 객체의 상호작용을 캡슐화하는 객체를 정의합니다. 객체ㅔ들이 직접 서로를 참조하지 않도록 하여 객체 사이의 소결합을 촉진시키며, 개발자가 객체의 상호작용을 독립적으로 다양화 시킬 수 있게 만듭니다.
1.1. 구조
Sample / Sequence Diagram
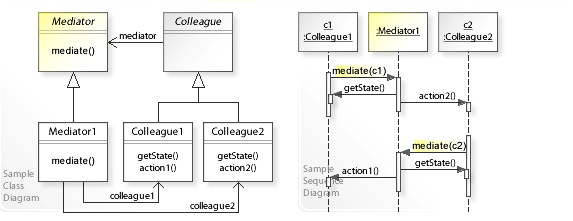
- Mediator
- Colleague 객체와 교류하는 데 필요한 인터페이스를 정의합니다.
- ConcreteMediator
- Colleague 객체와 조화를 이뤄서 협력 행동을 구현하며, 자신이 맡을 동료를 파악하고 관리합니다.
- Colleague
- 자신의 중재자 객체가 무엇인지 파악합니다. 다른 객체와 통신이 필요하면 그 중재자를 통해 통신되도록 하는 동료 객체를 나타내는 클래스입니다.
1.2. 사용 방법
- Colleague는 Mediator에서 요청을 송수신합니다. Mediator는 필요한 Colleague 사이에 요청을 전달할 의무가 있습니다.
1.3. 장/단점
- Advantages (+)
- Decouples colleagues.
- Centralizes interaction behavior.
- Makes changing the interaction behavior easy.
- Disadvantages (–)
- Can make the mediator complex.
1.4. 고려사항
- Consider the left design (problem):
- Tightly coupled colleagues.
- Distributed interaction behavior.
- Consider the right design (solution):
- Loosely coupled colleagues.
- Encapsulated interaction behavior.
2. 중재자 패턴(Mediator Pattern) 사용예시
중재자 패턴은 다음 경우에 사용합니다.
- 여러 객체가 잘 정의된 형태이기는 하지만 복잡한 상호작용을 가질 때
- 한 객체가 다른 객체를 너무 많이참조하고, 너무 많은 의사소통을 수행해서 그 객체를 재사용하기 힘들 때
- 여러 클래스에 분산된 행동들이 상속 없이 상황에 맞게 수정되어야 할 때
2.1. GOF 패턴
2.1.1. Mediator
abstract class Mediator {
// Mediating the interaction between colleagues.
public abstract void mediate(Colleague colleague);
}
2.1.2. ConcreteMediator
class Mediator1 extends Mediator {
private Colleague1 colleague1;
private Colleague2 colleague2;
void setColleagues(Colleague1 colleague1, Colleague2 colleague2) {
this.colleague1 = colleague1;
this.colleague2 = colleague2;
}
public void mediate(Colleague colleague) {
System.out.println(" Mediator : Mediating the interaction ...");
// Message from colleague1 that its state has changed.
if (colleague == colleague1) {
// Performing an action on colleague2.
String state = colleague1.getState();
colleague2.action2(state);
}
// Message from colleague2 that its state has changed.
if (colleague == colleague2) {
// Performing an action on colleague1.
String state = colleague2.getState();
colleague1.action1(state);
}
}
}
2.1.3. Colleague
abstract class Colleague {
Mediator mediator;
public Colleague(Mediator mediator) {
this.mediator = mediator;
}
}
class Colleague1 extends Colleague {
private String state;
public Colleague1(Mediator mediator) {
super(mediator); // Calling the super class constructor
}
public String getState() {
return state;
}
void setState(String state) {
if (state != this.state) {
this.state = state;
System.out.println(" Colleague1: My state changed to: " + this.state + " Calling my mediator ...");
mediator.mediate(this);
}
}
void action1 (String state) {
// For example, synchronizing and displaying state.
this.state = state;
System.out.println(" Colleague1: My state synchronized to: " + this.state);
}
}
class Colleague2 extends Colleague {
private String state;
public Colleague2(Mediator mediator) {
super(mediator); // Calling the super class constructor
}
public String getState() {
return state;
}
void setState(String state) {
if (state != this.state) {
this.state = state;
System.out.println(" Colleague2: My state changed to: " + this.state + " Calling my mediator ...");
mediator.mediate(this);
}
}
void action2 (String state) {
// For example, synchronizing and displaying state.
this.state = state;
System.out.println(" Colleague2: My state synchronized to: " + this.state);
}
}
2.1.4. Client
public class Main{
// Running the Client class as application.
public static void main(String[] args) {
Mediator1 mediator = new Mediator1();
// Creating colleagues
// and configuring them with a Mediator1 object.
Colleague1 c1 = new Colleague1(mediator);
Colleague2 c2 = new Colleague2(mediator);
// Setting mediator's colleagues.
mediator.setColleagues(c1, c2);
System.out.println("(1) Changing state of Colleague1 ...");
c1.setState("Hello World1!");
System.out.println("\n(2) Changing state of Colleague2 ...");
c2.setState("Hello World2!");
}
}
결과는 아래와 같습니다.
(1) Changing state of Colleague1 ...
Colleague1: My state changed to: Hello World1! Calling my mediator ...
Mediator : Mediating the interaction ...
Colleague2: My state synchronized to: Hello World1!
(2) Changing state of Colleague2 ...
Colleague2: My state changed to: Hello World2! Calling my mediator ...
Mediator : Mediating the interaction ...
Colleague1: My state synchronized to: Hello World2!
참고 자료
Leave a comment