디자인 패턴 톺아보기 - Flyweight Pattern
Updated:
1. 플라이웨이트 패턴(Flyweight Pattern) 이란?
GOF 에서 말하는 플라이웨이트 패턴의 목적은 아래와 같습니다.
Use sharing to support large numbers of fine-grained objects efficiently.
공유를 통해 많은 수의 소립(fine-grained) 객체들을 효과적으로 지원합니다.
1.1. 구조
Sample / Sequence Diagram
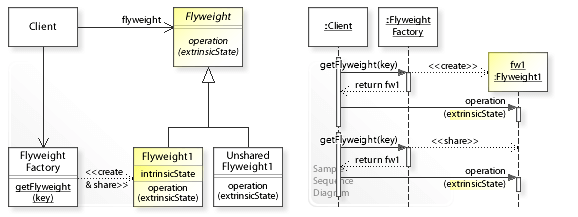
- Flyweight
- Flyweight 가 받아들일 수 있고, 부가적인 상태에서 동작해야 하는 인터페이스를 선언합니다.
- ConcreteFlyweight
- Flyweight 인터페이스를 구현하고 내부적으로 갖고 있어야 하는 본질적 사앹에 대한 저장소를 정의합니다. ConcreteFlyweight 객체는 공유할 수 있는 것이어야 합니다. 그러므로 관리하는 어떤 상태로도 본질적인 것이어야 합니다.
- UnsharedConcreteFlyweight
- 모든 플라이급 서브클래스들이 공유될 필요는 없습니다. Flyweight 인터페이스는 공유를 가능하게 하지만, 그것을 강요해서는 안 됩니다. UnsharedConcreteFlyweight 객체가 ConcreteFlyweight 객체를 자신의 자식으로 갖는 것은 흔한 일입니다.
- FlyweightFactory
- 플라이급 객체를 생성하고 관리하며, 플라이급 객체가 제대로 공유되도록 보장합니다. 사용자가 플라이급 객체를 요청하면 FlyweightFactory 객체는 이미 존재하는 인스턴스를 제공하거나 만약 존재하지 않는다면 새로 생성합니다.
- Client
- 플라이급 객체에 대한 참조자를 관리하며 플라이급 객체의 부가적 상태를 저장합니다.
1.2. 사용 방법
- 플라이급 객체가 기능을 수행하는 데 필요한 상태가 본질적인 것인지 부가적인것인지를 구분해야 합니다. 본질적 상태는 ConcreteFlyweight에 저장해야 하고, 부가적인 상태는 사용자가 저장하거나, 연산되어야 하는 다른 상태로 관리해야 합니다.
- 사용자는 연산을 호출할 때 자신에게만 필요한 부가적 상태를 플라이급 객체에 매개변수로 전달합니다.
- 사용자는 ConcreteFlyweight의 인스턴스를 직접 만들 수 없습니다. 사용자는 ConcreteFlyweight 객체를 FlyweightFactory 객체에서 얻어야 합니다. 이렇게 해야 플라이급 객체가 공유될 수 있습니다.
1.3. 장/단점
- Advantages (+)
- Enables abstractions at the finest levels
- Disadvantages (–)
- Introduces run-time costs
- Provides no reliability on object identity.
1.4. 고려사항
- Consider the left design (problem):
- Large number of physically created objects.
- Consider the right design (solution):
- Small number of physically created objects.
2. 플라이웨이트 패턴(Flyweight Pattern) 사용예시
플라이웨이트 패턴은 언제 사용하는가에 따라 그 효과가 달라집니다. 다음의 경우에 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 응용프로그램이 대량의 객체를 사용해야 할 때
- 객체의 수가 너무 많아져 저장 비용이 너무 높아질 때
- 대부분의 객체 상태를 부가적인 것으로 만들 수 있을 때
- 부가적인 속성들을 제거한 후 객체들을 조사해보니 객체의 많은 묶음이 비교적 적은 수의 공유된 객체로 대체될 수 있을 때
- 응용 프로그램이 객체의 정체성에 의존하지 않을 때
2.1. GOF 패턴
2.1.1. Flyweight
interface Flyweight {
public String operation(int extrinsicState);
}
2.1.2. ConcreteFlyweight
class ConcreteFlweight implements Flyweight {
private String intrinstcState;
public ConcreteFlweight(String intrinstcState) {
this.intrinstcState = intrinstcState ;
}
public String operation(int extrinsicState) {
return " performing an operation on the flyweight\n "
+ " with intrinsic state = " + this.intrinstcState
+ " and passed in extrinsic state = " + extrinsicState + ".";
}
}
2.1.3. FlyweightFactory
class FlyweightFactory {
// Implemented as Singleton.
// See also Singleton / Implementation / Variant 1.
private static final FlyweightFactory INSTANCE = new FlyweightFactory();
private FlyweightFactory() { }
public static FlyweightFactory getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}
// Shared flyweight pool.
private Map<String, Flyweight> flyweights = new HashMap<String, Flyweight>();
// Creating and maintaining shared flyweights.
public Flyweight getFlyweight(String key) {
if (flyweights.containsKey(key)) {
System.out.println("Sharing a flyweight with key = " + key);
return flyweights.get(key);
} else {
System.out.println("Creating a flyweight with key = " + key);
Flyweight flyweight = new ConcreteFlweight(key); // assuming key = intrinsic state
flyweights.put(key, flyweight);
return flyweight;
}
}
public int getSize() {
return flyweights.size();
}
}
2.1.4. Client
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Flyweight flyweight;
FlyweightFactory flyweightFactory = FlyweightFactory.getInstance();
flyweight = flyweightFactory.getFlyweight("A");
System.out.println(flyweight.operation(100));
flyweight = flyweightFactory.getFlyweight("A");
System.out.println(flyweight.operation(200));
flyweight = flyweightFactory.getFlyweight("B");
System.out.println("\n*** Number of flyweights created: " + flyweightFactory.getSize() + " ***");
}
}
결과는 아래와 같습니다.
Creating a flyweight with key = A
performing an operation on the flyweight
with intrinsic state = A and passed in extrinsic state = 100.
Sharing a flyweight with key = A
performing an operation on the flyweight
with intrinsic state = A and passed in extrinsic state = 200.
Creating a flyweight with key = B
*** Number of flyweights created: 2 ***
참고 자료
Leave a comment